What is Google Tag Manager (GTM) and Why do you need to use it?
Tháng 8 10, 2022
If you’ve never heard about Google Tag Manager (GTM), you are probably wondering what it is and why you should use it. Let’s dig around and find out how to utilize this amazing and free system.
What is Google Tag Manager (GTM)?
Google Tag Manager is a free tag management system that allows you to manage and deploy marketing tags (snippets of code or tracking pixels) on your website (or mobile app) without having to modify the code.
Here’s a very simple example of how Google Tag Manager works. Information from one data source (your website) is shared with another data source (Google Analytics) through Google Tag Manager. GTM becomes very handy when you have lots of tags to manage because all of the code is stored in one place.
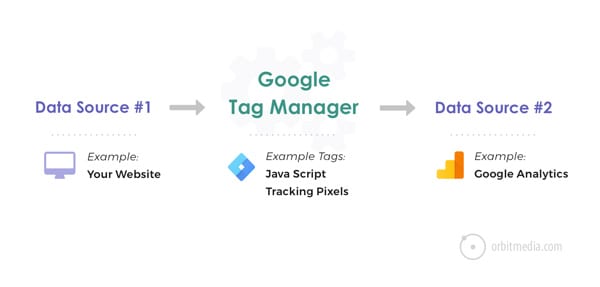
A huge benefit of Tag Manager is that you, the marketer, can manage the code on your own. “No more developers needed. Whoo hoo!”
Sounds easy right? Unfortunately, it’s not that simple.
Is Google Tag Manager easy to use?
According to Google,
“Google Tag Manager helps make tag management simple, easy và reliable by allowing marketers and webmasters to deploy website tags all in one place.”
They say it’s a “simple” tool that any marketer can use without needing a web developer.
I may get run over in the comments section for saying this, but I’m standing my ground. Google Tag Manager is not “easy” to use without some technical knowledge or training (courses or self-taught).
You have to have some technical knowledge to understand how to set up tags, triggers and variables. If you’re dropping in Facebook pixels, you’ll need some understanding of how Facebook tracking pixels work.
If you want to set up event tracking in Google Tag Manager, you’ll need some knowledge about what “events” are, how Google Analytics works, what data you can track with events, what the reports look like in Google Analytics and how to name your categories, actions and labels.
Although it is “easy” to manage multiple tags in GTM, there is a learning curve. Once you’re over the hump, GTM is pretty slick about what you can track.
Let’s go over how Google Tag Manager works…
There are three main parts to Google Tag Manager:
- Tags: Snippets of Javascript or tracking pixels
- Triggers: This tells Google Tag Manager when, where or how to fire a tag
- Variables: Additional information GTM may need for the tag and trigger to work
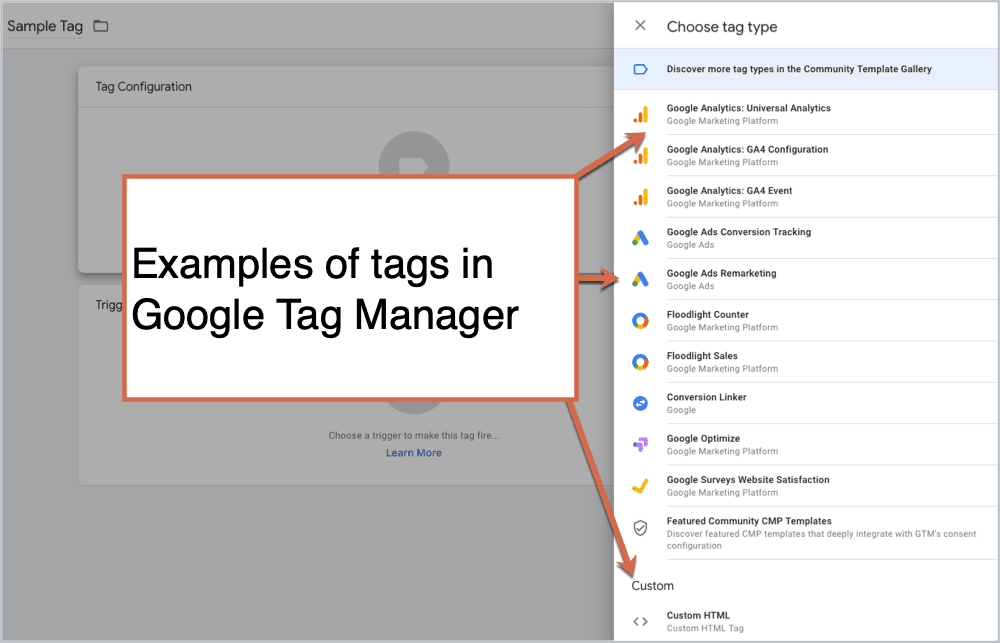
What are tags?
Tags are snippets of code or tracking pixels from third-party tools. These tags tell Google Tag Manager what to do.
Examples of common tags within Google Tag Manager are:
- Google Analytics Universal tracking code or GA4 tracking code
- Adwords Remarketing code
- Adwords Conversion Tracking code
- Heatmap tracking code (Hotjar, CrazyEgg, etc…)
- Facebook pixels
- Custom HTML scripts
- Cookiebot and other GDPR data privacy scripts
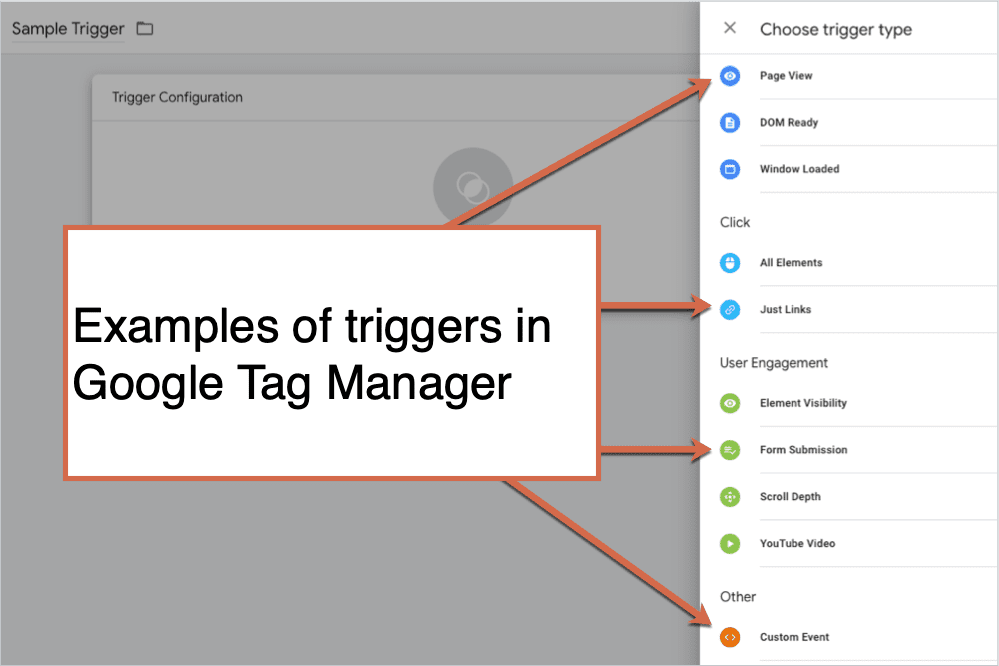
What are triggers?
Triggers are a way to fire the tag that you set up. They tell Tag Manager when, where or how to do what you want it to do. Want to fire tags on a page view, link click or is it custom?
Examples of common triggers within Google Tag Manager are:
- Pageviews
- Links clicks
- Form submissions
- Scroll depth
- Custom events
What are variables?
Variables are additional information that GTM may need for your tag and trigger to work. Here are some examples of different variables.
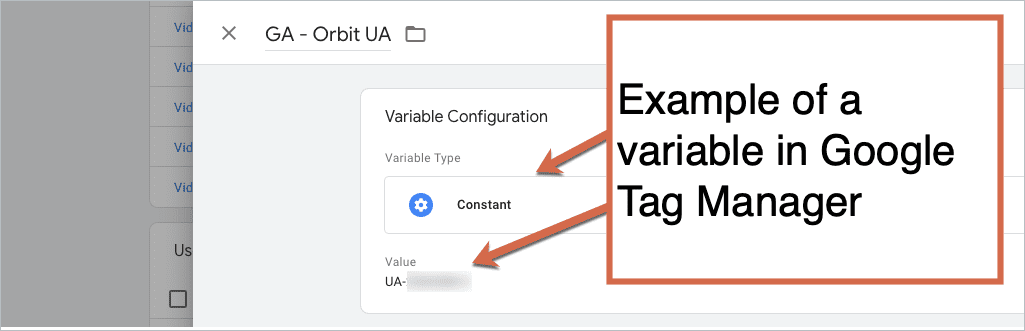
The most basic type of variable that you can create in GTM is the Google Analytics UA number (the tracking ID number).
Those are the very basic elements of GTM that you will need to know to start managing tags on your own.
If you’re bored reading this right now, you won’t have any issues managing your tags. If you are completely lost, you are going to need help from someone more technical.
How is Google Tag Manager different from Google Analytics?
Google Tag Manager is a completely different tool used only for storing and managing third-party code. There are no reports or any way to do analysis in GTM.
Google Analytics is used for actual reporting and analysis. All conversion tracking goals or filters are managed through Analytics.
All reporting (conversion reports, custom segments, ecommerce sales, time on page, engagement reports, etc…) are done in Google Analytics.

What are the benefits of Google Tag Manager?
Once you get over the learning curve, what you can do in Google Tag Manager is pretty amazing. You can customize the data that is sent to Analytics.
You can set up and track basic events like PDF downloads, outbound link clicks or button clicks. Or, complex enhanced ecommerce product and promotion tracking.
Let’s say we want to track all outbound links on the website. In GTM, choose the category name, action and label. We chose offsite link, click and click URL.
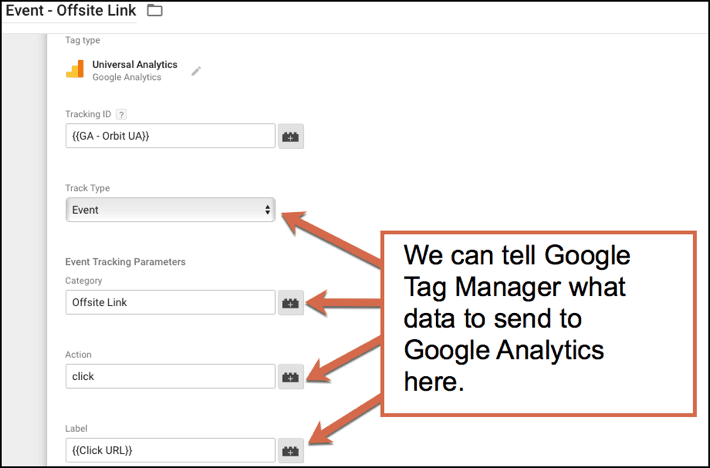
In Google Analytics go to Behavior > Events > Top Events > Offsite link.
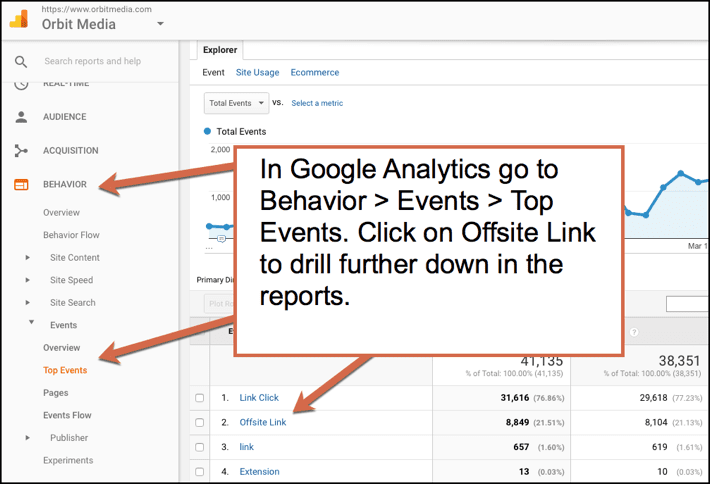
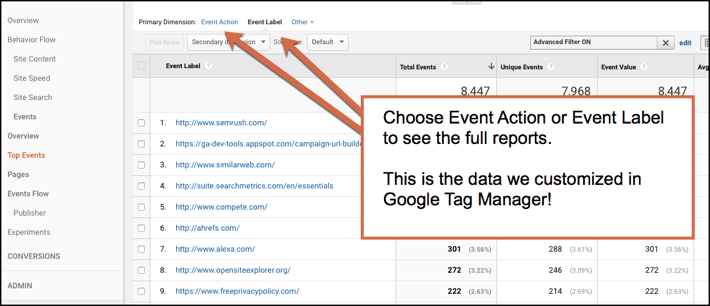
Now select either event action or label to get the full reports. The data that we set up in Google Tag Manager is now appearing in the Analytics reports. Nifty!
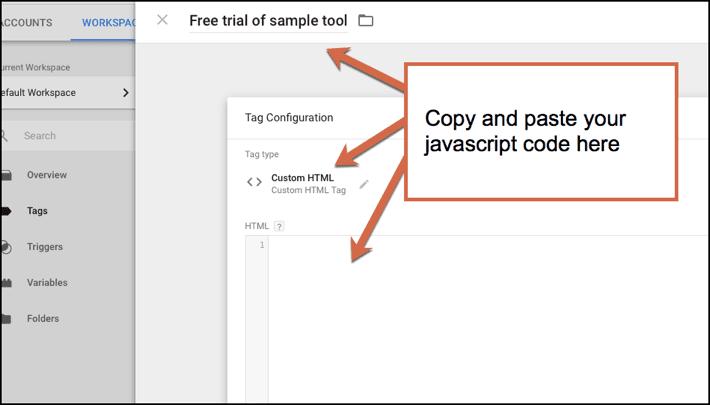
Want to try out a tool on a free trial basis? You can add the code to Tag Manager and test it out without needing to get your developers involved.
Other perks:
- It may help your site load faster depending on how many tags you are using.
- It works with non-Google products.
- Flexibility to play around and test out almost anything you want.
- All third-party code is in one place.
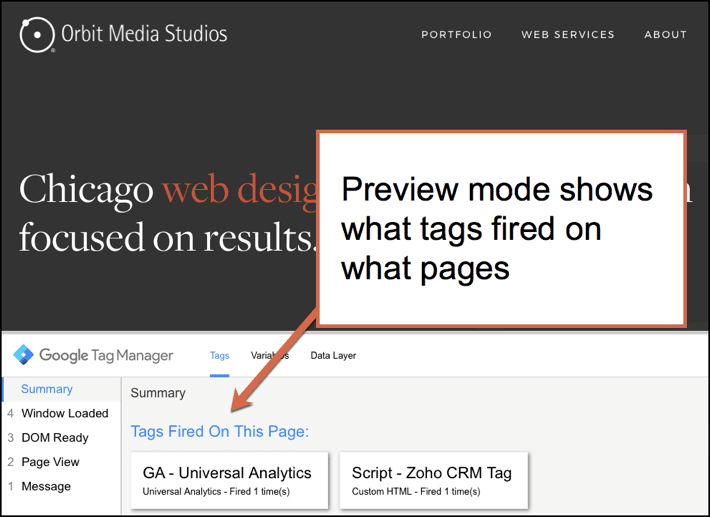
- GTM has a preview and debug mode so you can see what’s working and what’s not before you make anything live. It shows you what tags are firing on the page. Love this feature!
What are the drawbacks?
1. You must have some technical knowledge, even for the basic setup.
Check out the documentation from Google on how to setup Google Tag Manager. Once you get past the “Quick Start Guide,” it takes you to a developer guide. Not a marketer’s guide. If you are a first time user, this will read like gibberish.
2. It’s a time investment.
Unless you’re a seasoned developer, you will need to carve out a chunk of research and testing time. Even if it’s reading a few blog posts or taking an online class.
3. Make time for troubleshooting issues.
There is a lot of troubleshooting that takes place when setting up tags, triggers and variables. Especially if you are not in Tag Manager regularly, it’s very easy to forget what you just learned. For more complex tags, you will likely need a developer with knowledge of how the website was built.
What can you track in Google Tag Manager (GTM)?
- Events (link clicks, PDF downloads, add to cart click, remove from cart click)
- Scroll tracking
- Form abandonment
- Shopping cart abandonment
- Video views tracking
- All exit link clicks
- …??????
We are just scratching the surface of what you can do in Google Tag Manager. The possibilities seem almost endless. But, as Himanshu Sharma points out, the more tags and data sources you have the harder they are to manage.
Where can I learn more about Google Tag Manager?
I took a live course through Conversion XL with Chris Mercer. It was one of the best online classes I’ve taken. You can purchase the recordings if you are interested.
Other go-to resources are:
- Himanshu Sharma, Optimize Smart blog
- Simo Hava blog
- Conversion XL blog
- Chris Mercer, Seriously Simple Marketing
- AnalyticsPros blog
Your turn. What do you think of Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager can definitely make your life easier if you are willing to learn how it works. Make sure that you are actually using the data that you are setting up in GTM. Otherwise, what’s the point?
I’m curious to hear your experience with Google Tag Manager. Has it been easy or hard? How are you using it in your marketing?
Article by Amanda Gant of Orbit Media